目次
32.vsftp設定
/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf設定
#インストール dnf install vsftpd #設定変更 vi /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf vi /etc/vsftpd/chroot_list vi /etc/vsftpd/user_list vi /etc/vsftpd/ftpusers #適用/有効化 systemctl restart vsftpd systemctl enable vsftpd
ローカルユーザがログインした後に移動するディレクトリを、ローカルユーザのホームディレクトリにする。
/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf設定詳細
vsftpdの設定詳細について記載する。
設定については、下記サイトを参考にしました。
http://www.nina.jp/server/redhat/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf.html
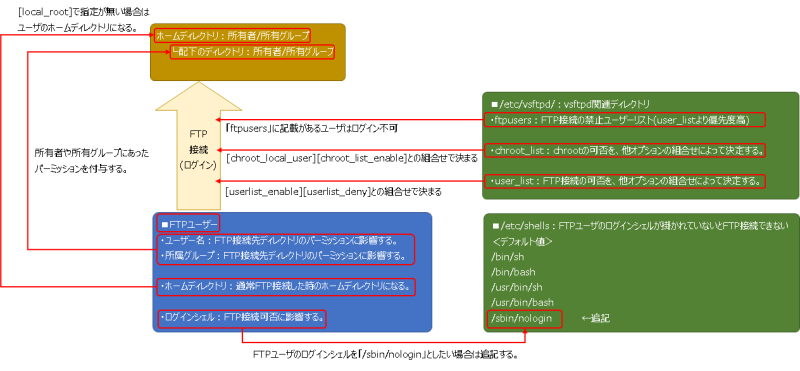
■概要
・匿名ユーザー:関連の設定は全て許可しない
・FTPサーバ(FTPSにしていない)
・パッシブモード(ポート範囲を指定)
・ログ取得:vsftpd.logにのみ出力
・chroot:全てのローカルユーザが対象(chroot_listは影響させない)
・移動ディレクトリ:ローカルユーザのホームディレクトリ
・ログイン許可:user_listに含まれるローカルユーザーアカウントのみ可能
・ログイン拒否:ftpusersに含まれるローカルユーザーアカウントが拒否される
- 開く
-
#匿名ユーザー関連 #AnonymousのFTPログインの許可するか anonymous_enable=NO #Anonymousのファイル書き込み許可するか anon_upload_enable=NO #Anonymousのディレクトリの生成を許可するか anon_mkdir_write_enable=NO #Anonymousでアップロードされたファイルの所有者 chown_username=root #Anonymousでアップロードされたファイルの所有者変更を有効にするか chown_uploads=YES ###ログ取得設定(この組合せで[vsftpd_log_file]の指定先ファイルにのみ出力するという意味) xferlog_enable=YES syslog_enable=NO dual_log_enable=NO xferlog_std_format=NO #ログファイルの出力先 #xferlog_file=/var/log/xferlog vsftpd_log_file=/var/log/vsftpd.log ###asciiモード関連 #ダウンロードを許可するか #ascii_upload_enable=YES #アップロードを許可するか #ascii_download_enable=YES ###chroot関連(下記の組合せで、全てのローカルユーザはchrootされるという意味) chroot_local_user=YES chroot_list_enable=NO #chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list #chrootした先に書込み権限があってもFTP接続可能にするか allow_writeable_chroot=YES ###ログイン可否関連(下記の組合せで、user_listに含まれるユーザのみ許可という意味) userlist_enable=YES userlist_deny=NO userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd/user_list #アクティブモード時のポート番号 #connect_from_port_20=YES #PASVコマンドの応答でクライアントに通知する、サーバのIPアドレスを指定する。 pasv_address=[グローバルIPアドレス] #PASVデータコネクションで使用する、最大ポートと最小ポートを指定する。 pasv_min_port=65000 pasv_max_port=65535 #ローカルユーザアカウントによるログインを許可するか local_enable=YES #ファイルに変更を加えるFTPコマンドの使用を許可するか write_enable=YES #新規ファイルに適用するパーミッションのumask値 local_umask=022 #接続先ディレクトリにメッセージファイルがあった場合表示するか dirmessage_enable=NO #コントロールコネクションの応答がない場合のタイムアウト値 idle_session_timeout=300 #データ転送の応答がない場合のタイムアウト値 data_connection_timeout=120 #vsftpdが使用する非特権ユーザ nopriv_user=nobody #asyncABOR"コマンドを有効にするか async_abor_enable=YES #FTP接続した際にメッセージを表示するか #ftpd_banner=WelcometoblahFTPservice. #ログインを拒否するメールアドレスのリスト #banned_email_file=/etc/vsftpd/banned_emails #ログインを拒否するメールアドレスのリストを有効にするか #deny_email_enable=YES #[ls-R]コマンドを許可するか #ls_recurse_enable=YES #vsftpdをスタンドアロンモードで起動するか(NOの場合はスーパーデーモン) listen=YES #IPv6で動作するか(NOの場合はIPv4) listen_ipv6=NO #vsftpdが使用するPAMサービス名 pam_service_name=vsftpd #全てののローカルユーザが、ログインした後に移動するディレクトリ #local_root=/home/%u
例:設定の流れ
「/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf設定詳細」が設定済みの前提で記載します。
FTP用ユーザ(webadmin)を作成し、「/var/www/html」配下の「web」ディレクトリのみに読み書き可能な環境を作成する流れになります。
- 開く
-
#FTP用ユーザ(webadmin)を作成、合わせて、「/var/www/html」配下の「web」ディレクトリを作成する。 useradd -s /sbin/nologin -d /var/www/html/web -m webadmin #sshは利用しないので、プロファイル(.bash_logout、.bash_profile、.bashrc)は消す。 rm -f /var/www/html/web/* #「/var/www/html/web」のパーミッション変更 chmod 755 /var/www/html/web #パスワードの設定/変更 passwd webadmin #「/etc/shells」を変更し「/sbin/nologin」を追記する。 vi /etc/shells #「/etc/vsftpd/user_list」を変更し「webadmin」を追記する。 vi /etc/vsftpd/user_list
ローカルユーザがログインした後に移動するディレクトリを、user_configで指定したディレクトリにする。
/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf設定詳細
vsftpdの設定詳細について記載する。
設定については、下記サイトを参考にしました。
http://www.nina.jp/server/redhat/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf.html
■概要
・匿名ユーザー:関連の設定は全て許可しない
・FTPサーバ(FTPSにしていない)
・パッシブモード(ポート範囲を指定)
・ログ取得:vsftpd.logにのみ出力
・chroot:全てのローカルユーザが対象(chroot_listは影響させない)
・移動ディレクトリ:user_configで指定したディレクトリ
・ログイン許可:user_listに含まれるローカルユーザーアカウントのみ可能
・ログイン拒否:ftpusersに含まれるローカルユーザーアカウントが拒否される
- 開く
-
#匿名ユーザー関連 #AnonymousのFTPログインの許可するか anonymous_enable=NO #Anonymousのファイル書き込み許可するか anon_upload_enable=NO #Anonymousのディレクトリの生成を許可するか anon_mkdir_write_enable=NO #Anonymousでアップロードされたファイルの所有者 chown_username=root #Anonymousでアップロードされたファイルの所有者変更を有効にするか chown_uploads=YES ###ログ取得設定(この組合せで[vsftpd_log_file]の指定先ファイルにのみ出力するという意味) xferlog_enable=YES syslog_enable=NO dual_log_enable=NO xferlog_std_format=NO #ログファイルの出力先 #xferlog_file=/var/log/xferlog vsftpd_log_file=/var/log/vsftpd.log ###asciiモード関連 #ダウンロードを許可するか #ascii_upload_enable=YES #アップロードを許可するか #ascii_download_enable=YES ###chroot関連(下記の組合せで、全てのローカルユーザはchrootされるという意味) chroot_local_user=YES chroot_list_enable=NO #chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list #chrootした先に書込み権限があってもFTP接続可能にするか allow_writeable_chroot=YES ###ログイン可否関連(下記の組合せで、user_listに含まれるユーザのみ許可という意味) userlist_enable=YES userlist_deny=NO #userlist_file=/etc/vsftpd/user_list #ユーザごとの設定を記述したファイルを置くディレクトリを指定する。 user_config_dir=/etc/vsftpd/user_conf #アクティブモード時のポート番号 #connect_from_port_20=YES #PASVコマンドの応答でクライアントに通知する、サーバのIPアドレスを指定する。 pasv_address=[グローバルIPアドレス] #PASVデータコネクションで使用する、最大ポートと最小ポートを指定する。 pasv_min_port=65000 pasv_max_port=65535 #ローカルユーザアカウントによるログインを許可するか local_enable=YES #ファイルに変更を加えるFTPコマンドの使用を許可するか write_enable=YES #新規ファイルに適用するパーミッションのumask値 local_umask=022 #接続先ディレクトリにメッセージファイルがあった場合表示するか dirmessage_enable=NO #コントロールコネクションの応答がない場合のタイムアウト値 idle_session_timeout=300 #データ転送の応答がない場合のタイムアウト値 data_connection_timeout=120 #vsftpdが使用する非特権ユーザ nopriv_user=nobody #asyncABOR"コマンドを有効にするか async_abor_enable=YES #FTP接続した際にメッセージを表示するか #ftpd_banner=WelcometoblahFTPservice. #ログインを拒否するメールアドレスのリスト #banned_email_file=/etc/vsftpd/banned_emails #ログインを拒否するメールアドレスのリストを有効にするか #deny_email_enable=YES #[ls-R]コマンドを許可するか #ls_recurse_enable=YES #vsftpdをスタンドアロンモードで起動するか(NOの場合はスーパーデーモン) listen=YES #IPv6で動作するか(NOの場合はIPv4) listen_ipv6=NO #vsftpdが使用するPAMサービス名 pam_service_name=vsftpd #全てののローカルユーザが、ログインした後に移動するディレクトリ #local_root=/home/%u
例:設定の流れ
「/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf設定詳細」が設定済みの前提で記載します。
FTP用ユーザ(webadmin)を作成し、「/var/www/html」配下の「web」ディレクトリのみに読み書き可能な環境を作成する流れになります。
- 開く
-
#FTP用ユーザ(webadmin)を作成する。 useradd -s /sbin/nologin -m webadmin #ログインした後に移動するディレクトリを作成 mkdir -p -m 755 /var/www/html/web #「/var/www/html/web」の所有者を変更 chown webadmin:webadmin /var/www/html/web #パスワードの設定/変更 passwd webadmin #「/etc/shells」を変更し「/sbin/nologin」を追記する。 vi /etc/shells #「/etc/vsftpd/user_list」を変更し「webadmin」を追記する。 vi /etc/vsftpd/user_list #user_conf用ディレクトリ作成 mkdir /etc/vsftpd/user_conf #「webadmin」用の設定ファイルを作成し、移動するディレクトリ「local_root=/var/www/html/web」を追記する。 vi /etc/vsftpd/user_conf/webadmin
初期値
- 開く
-
# Example config file /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf # # The default compiled in settings are fairly paranoid. This sample file # loosens things up a bit, to make the ftp daemon more usable. # Please see vsftpd.conf.5 for all compiled in defaults. # # READ THIS: This example file is NOT an exhaustive list of vsftpd options. # Please read the vsftpd.conf.5 manual page to get a full idea of vsftpd's # capabilities. # # Allow anonymous FTP? (Beware - allowed by default if you comment this out). anonymous_enable=NO # # Uncomment this to allow local users to log in. local_enable=YES # # Uncomment this to enable any form of FTP write command. write_enable=YES # # Default umask for local users is 077. You may wish to change this to 022, # if your users expect that (022 is used by most other ftpd's) local_umask=022 # # Uncomment this to allow the anonymous FTP user to upload files. This only # has an effect if the above global write enable is activated. Also, you will # obviously need to create a directory writable by the FTP user. # When SELinux is enforcing check for SE bool allow_ftpd_anon_write, allow_ftpd_full_access #anon_upload_enable=YES # # Uncomment this if you want the anonymous FTP user to be able to create # new directories. #anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES # # Activate directory messages - messages given to remote users when they # go into a certain directory. dirmessage_enable=YES # # Activate logging of uploads/downloads. xferlog_enable=YES # # Make sure PORT transfer connections originate from port 20 (ftp-data). connect_from_port_20=YES # # If you want, you can arrange for uploaded anonymous files to be owned by # a different user. Note! Using "root" for uploaded files is not # recommended! #chown_uploads=YES #chown_username=whoever # # You may override where the log file goes if you like. The default is shown # below. #xferlog_file=/var/log/xferlog # # If you want, you can have your log file in standard ftpd xferlog format. # Note that the default log file location is /var/log/xferlog in this case. xferlog_std_format=YES # # You may change the default value for timing out an idle session. #idle_session_timeout=600 # # You may change the default value for timing out a data connection. #data_connection_timeout=120 # # It is recommended that you define on your system a unique user which the # ftp server can use as a totally isolated and unprivileged user. #nopriv_user=ftpsecure # # Enable this and the server will recognise asynchronous ABOR requests. Not # recommended for security (the code is non-trivial). Not enabling it, # however, may confuse older FTP clients. #async_abor_enable=YES # # By default the server will pretend to allow ASCII mode but in fact ignore # the request. Turn on the below options to have the server actually do ASCII # mangling on files when in ASCII mode. The vsftpd.conf(5) man page explains # the behaviour when these options are disabled. # Beware that on some FTP servers, ASCII support allows a denial of service # attack (DoS) via the command "SIZE /big/file" in ASCII mode. vsftpd # predicted this attack and has always been safe, reporting the size of the # raw file. # ASCII mangling is a horrible feature of the protocol. #ascii_upload_enable=YES #ascii_download_enable=YES # # You may fully customise the login banner string: #ftpd_banner=Welcome to blah FTP service. # # You may specify a file of disallowed anonymous e-mail addresses. Apparently # useful for combatting certain DoS attacks. #deny_email_enable=YES # (default follows) #banned_email_file=/etc/vsftpd/banned_emails # # You may specify an explicit list of local users to chroot() to their home # directory. If chroot_local_user is YES, then this list becomes a list of # users to NOT chroot(). # (Warning! chroot'ing can be very dangerous. If using chroot, make sure that # the user does not have write access to the top level directory within the # chroot) #chroot_local_user=YES #chroot_list_enable=YES # (default follows) #chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list # # You may activate the "-R" option to the builtin ls. This is disabled by # default to avoid remote users being able to cause excessive I/O on large # sites. However, some broken FTP clients such as "ncftp" and "mirror" assume # the presence of the "-R" option, so there is a strong case for enabling it. #ls_recurse_enable=YES # # When "listen" directive is enabled, vsftpd runs in standalone mode and # listens on IPv4 sockets. This directive cannot be used in conjunction # with the listen_ipv6 directive. listen=NO # # This directive enables listening on IPv6 sockets. By default, listening # on the IPv6 "any" address (::) will accept connections from both IPv6 # and IPv4 clients. It is not necessary to listen on *both* IPv4 and IPv6 # sockets. If you want that (perhaps because you want to listen on specific # addresses) then you must run two copies of vsftpd with two configuration # files. # Make sure, that one of the listen options is commented !! listen_ipv6=YES pam_service_name=vsftpd userlist_enable=YES
コメント